Adding autoparking model and world
Adding autoparking model and world
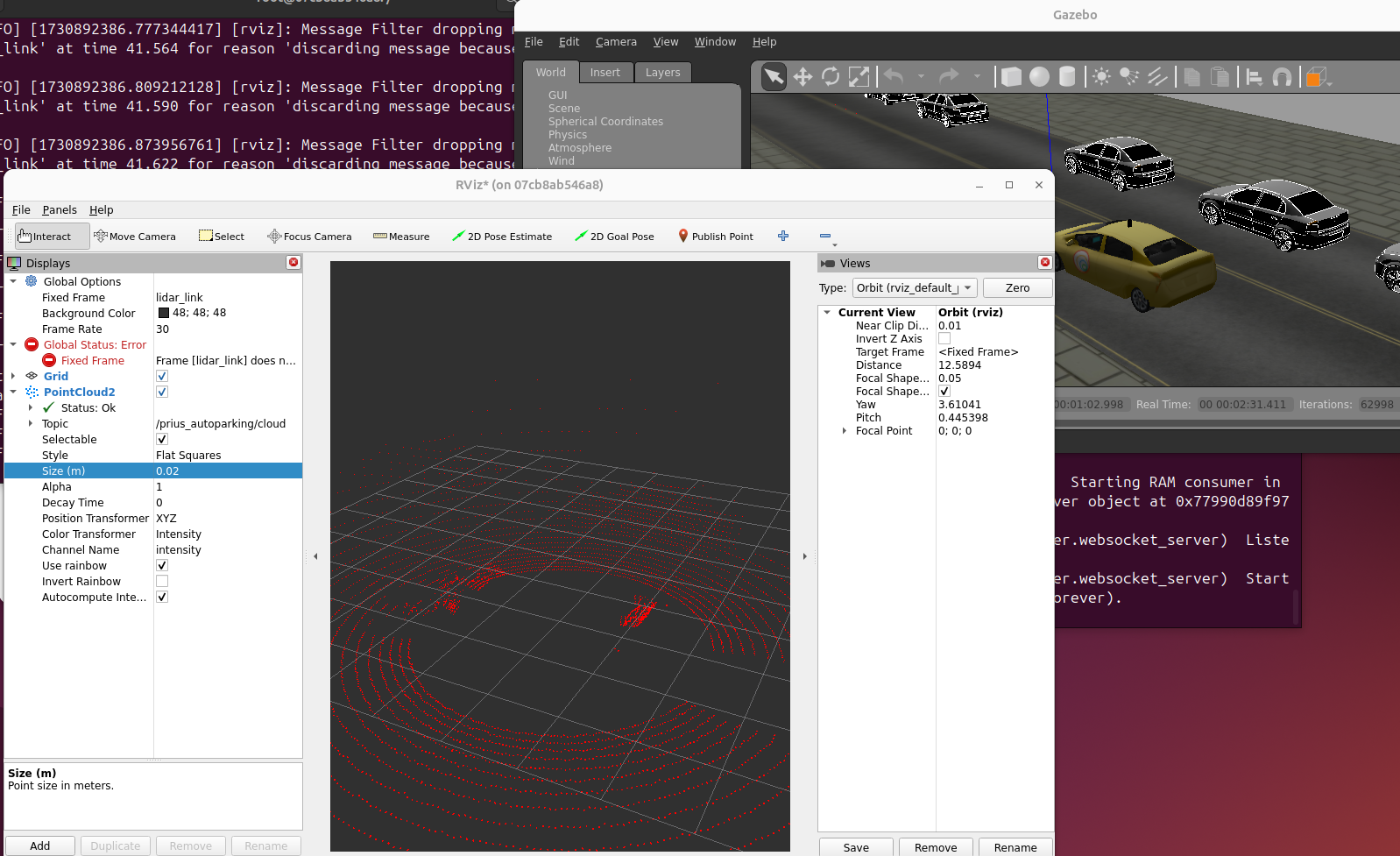
This week I created a world and a model for the autoparking exercise. The world is the same as the one used in the autoparking exercise but with the new model as the controllable car instead of the old one. This new model is a car with a 360 degree 3D LIDAR sensor, gathering the information around the car as a point cloud message.
Creating the model
After spending a lot of time, the way to create de model was quite simple. Since the model that I needed was the same as the one in the autoparking exercise, I just took that model (prius_ackerman_3laser) from the Robotics Infrastructure repository. I removed two of the laser sensors and modified the last one so it’s positioned at the top of the car (in the model.sdf file).
Then, I changed the min_angle and max_angle parameters in the horizontal parameter of the sensor, so it covers 360 degrees in the horizontal plane. Then, to make it 3D, I added a vertical parameter to the sensor, with the angle parameters set in a way so it covers all around the car. Lastly on the plugin parameter, in the output I changed it into sensor_msgs/PointCloud2.
To create the world I also copied the world autoparking_prius_3laser.world and replaced the car model it spawns (prius_ackerman_3laser) with the new one.
Testing the model
Next I had to test the world in a Robotics Backend container to see if it works. To do that, I pulled a Robotics Backend image.
1
docker pull jderobot/robotics-backend:latest
Then, we run the docker container like this.
1
docker run --rm -it -p 7164:7164 -p 6000:6000 -p 1108:1108 -p 7163:7163 -v /tmp/.X11-unix:/tmp/.X11-unix -e DISPLAY=$DISPLAY -v (path to directory with model and world):(path inside docker) jderobot/robotics-backend
This command is a bit different than the usual way you can use the docker run command to run the container. The .X11-unix stuff and DISPLAY are used to let you run gazebo inside the container and see the GUI in your desktop. The other -v argument copies de contents of the directory with my model and world and paste it inside the path indicated by (path inside docker), that way we can use the model and world inside the container. After that, we run these commands on another terminal.
1
2
xhost +local:root
docker exec (container id) bash
We only have to execute the first command once, since it’s another step to let us visualize the Gazebo GUI from the docker in our desktop. The second command is for running a bash terminal inside the container. Now we can run gazebo inside the container with the world I created to see the results. To do that, go to the directory created inside the container with the model and run this:
1
export GAZEBO_MODEL_PATH=:$(pwd):/home/ws/src/CustomRobots/ackermann_cars/models:/home/ws/src/CustomRobots/autoparking/models:/home/ws/src/CustomRobots/car_junction/models
This lets gazebo find all the models needed to run the world. We can run another bash terminal and use rviz to see the sensor output. Make sure to have lidar_link as the Fixed Frame.