Coding week2 6/03-6/09
Weekly Meeting
In this week’s meeting, we reviewed our project’s current status. We analyzed the high similarity observed in the outputs generated by GPT and discussed the issues of data distribution, which led to redundancy. To address these concerns, we brainstormed strategies to enhance the diversity and balance of our dataset. Additionally, we revisited four key commands from our previous project and explored how integrating more commands could boost both functionality and efficiency. We also deliberated on setting appropriate metrics for the BERT model by segmenting the dataset into training and testing sets.
More details can be found here: Google Doc
To-Do List
- Generate scalable datasets that are intertwined with actions and commands with LLMs.
- Perform quality analyses on the generated datasets.
- Train the Bert model to classify instructions and obtain a model.
- Move training and test notebooks in gsoc23 to a separate script. issue
Progress
This week, I developed a module designed to generate user-driving instructions using GPT. The code focuses on creating prompts based on predefined templates and user inputs, with an emphasis on improving the logic for prompt creation to enhance clarity and engagement. Additionally, the module includes features for validating user inputs and adjusting the output format accordingly. This advancement is beneficial for providing scalable instruction datasets in our project.
The module also implements an action generation component, which formulates specific actions based on the instructions generated by GPT, such as “turn left,” “turn right,” “take exit,” “go straight,” “accelerate,” and “slow down.” Furthermore, I developed analytical tools within the prompt_analysis.py script to evaluate the effectiveness of the generated instructions, incorporating metrics to assess their relevance. Lastly, I implemented training using the BERT model to further enhance the module’s performance.
python train.py
1000 1000
Labels length: 1000
Input IDs length: 1000
Attention Mask length: 1000
Some weights of BertForSequenceClassification were not initialized from the model checkpoint at bert-base-uncased and are newly initialized: ['classifier.bias', 'classifier.weight']
You should probably TRAIN this model on a down-stream task to be able to use it for predictions and inference.
{'loss': 1.697, 'grad_norm': 19.306570053100586, 'learning_rate': 1.0000000000000002e-06, 'epoch': 0.09}
{'loss': 1.617, 'grad_norm': 13.708064079284668, 'learning_rate': 2.0000000000000003e-06, 'epoch': 0.18}
{'loss': 1.4665, 'grad_norm': 9.595329284667969, 'learning_rate': 3e-06, 'epoch': 0.27}
{'loss': 1.2224, 'grad_norm': 12.889700889587402, 'learning_rate': 4.000000000000001e-06, 'epoch': 0.35}
{'loss': 1.0262, 'grad_norm': 10.967733383178711, 'learning_rate': 5e-06, 'epoch': 0.44}
{'loss': 0.7739, 'grad_norm': 13.827258110046387, 'learning_rate': 6e-06, 'epoch': 0.53}
{'loss': 0.7852, 'grad_norm': 5.5881853103637695, 'learning_rate': 7.000000000000001e-06, 'epoch': 0.62}
{'loss': 0.6525, 'grad_norm': 8.820500373840332, 'learning_rate': 8.000000000000001e-06, 'epoch': 0.71}
{'loss': 0.3866, 'grad_norm': 4.9470295906066895, 'learning_rate': 9e-06, 'epoch': 0.8}
{'loss': 0.3203, 'grad_norm': 3.308020830154419, 'learning_rate': 1e-05, 'epoch': 0.88}
{'loss': 0.3612, 'grad_norm': 9.319038391113281, 'learning_rate': 1.1000000000000001e-05, 'epoch': 0.97}
{'loss': 0.3051, 'grad_norm': 8.626148223876953, 'learning_rate': 1.2e-05, 'epoch': 1.06}
{'loss': 0.3143, 'grad_norm': 4.779806613922119, 'learning_rate': 1.3000000000000001e-05, 'epoch': 1.15}
{'loss': 0.2742, 'grad_norm': 8.452868461608887, 'learning_rate': 1.4000000000000001e-05, 'epoch': 1.24}
{'loss': 0.3953, 'grad_norm': 3.7451024055480957, 'learning_rate': 1.5e-05, 'epoch': 1.33}
{'loss': 0.2989, 'grad_norm': 0.8715028762817383, 'learning_rate': 1.6000000000000003e-05, 'epoch': 1.42}
{'loss': 0.3149, 'grad_norm': 9.316072463989258, 'learning_rate': 1.7000000000000003e-05, 'epoch': 1.5}
{'loss': 0.1399, 'grad_norm': 8.054197311401367, 'learning_rate': 1.8e-05, 'epoch': 1.59}
{'loss': 0.246, 'grad_norm': 7.560857772827148, 'learning_rate': 1.9e-05, 'epoch': 1.68}
{'loss': 0.151, 'grad_norm': 0.3591634929180145, 'learning_rate': 2e-05, 'epoch': 1.77}
{'loss': 0.1007, 'grad_norm': 7.88149881362915, 'learning_rate': 2.1e-05, 'epoch': 1.86}
63%|█████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████▏ | 215/33 64%|████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████▉ | 216/339 [00:55<00:31, 3.93it/s]{'loss': 0.1223, 'grad_norm': 1.4635449647903442, 'learning_rate': 2.2000000000000003e-05, 'epoch': 1.95}
{'loss': 0.1039, 'grad_norm': 17.848655700683594, 'learning_rate': 2.3000000000000003e-05, 'epoch': 2.04}
{'loss': 0.2297, 'grad_norm': 0.22711549699306488, 'learning_rate': 2.4e-05, 'epoch': 2.12}
{'loss': 0.2394, 'grad_norm': 0.3263954222202301, 'learning_rate': 2.5e-05, 'epoch': 2.21}
{'loss': 0.2566, 'grad_norm': 0.4583888351917267, 'learning_rate': 2.6000000000000002e-05, 'epoch': 2.3}
{'loss': 0.1733, 'grad_norm': 0.12949731945991516, 'learning_rate': 2.7000000000000002e-05, 'epoch': 2.39}
{'loss': 0.1403, 'grad_norm': 0.12070054560899734, 'learning_rate': 2.8000000000000003e-05, 'epoch': 2.48}
{'loss': 0.2578, 'grad_norm': 0.15354938805103302, 'learning_rate': 2.9e-05, 'epoch': 2.57}
{'loss': 0.1055, 'grad_norm': 0.30441755056381226, 'learning_rate': 3e-05, 'epoch': 2.65}
{'loss': 0.2079, 'grad_norm': 16.82185935974121, 'learning_rate': 3.1e-05, 'epoch': 2.74}
{'loss': 0.2025, 'grad_norm': 4.622957229614258, 'learning_rate': 3.2000000000000005e-05, 'epoch': 2.83}
{'loss': 0.1915, 'grad_norm': 18.763633728027344, 'learning_rate': 3.3e-05, 'epoch': 2.92}
{'train_runtime': 84.7519, 'train_samples_per_second': 31.858, 'train_steps_per_second': 4.0, 'train_loss': 0.45582248397984687, 'epoch': 3.0}
100%|██████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████| 339/339 [01:24<00:00, 4.00it/s]
100%|██████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████| 7/7 [00:00<00:00, 11.49it/s]
100%|██████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████| 7/7 [00:00<00:00, 11.14it/s]
precision recall f1-score support
0 0.99 0.96 0.97 89
1 0.71 0.91 0.80 11
accuracy 0.95 100
macro avg 0.85 0.93 0.89 100
weighted avg 0.96 0.95 0.95 100
Challenges
During the data generation process, I encountered a significant issue with data imbalance. By using GPT to generate 1000 data points, I discovered that the distribution of the data was uneven, as illustrated below:
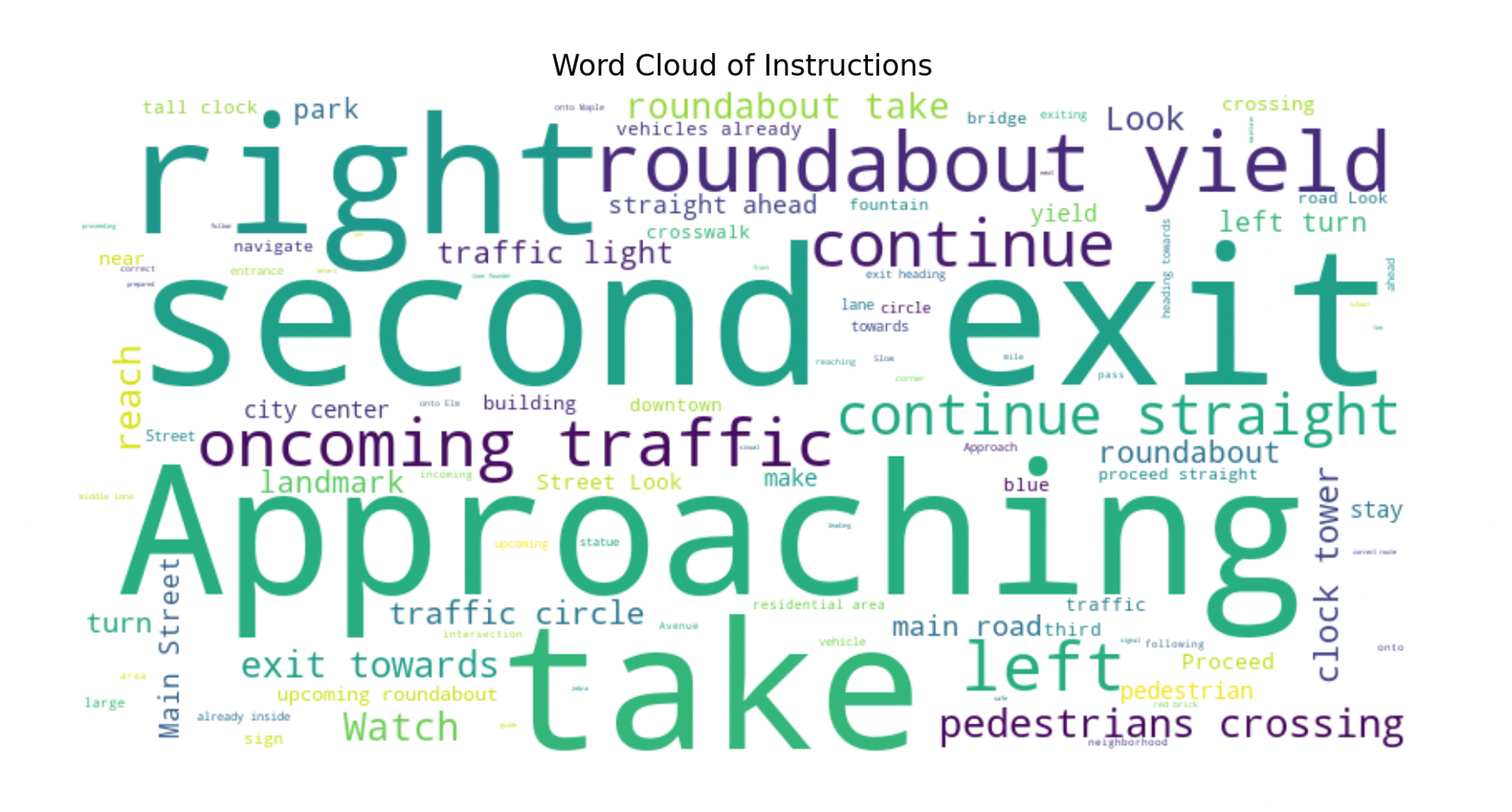
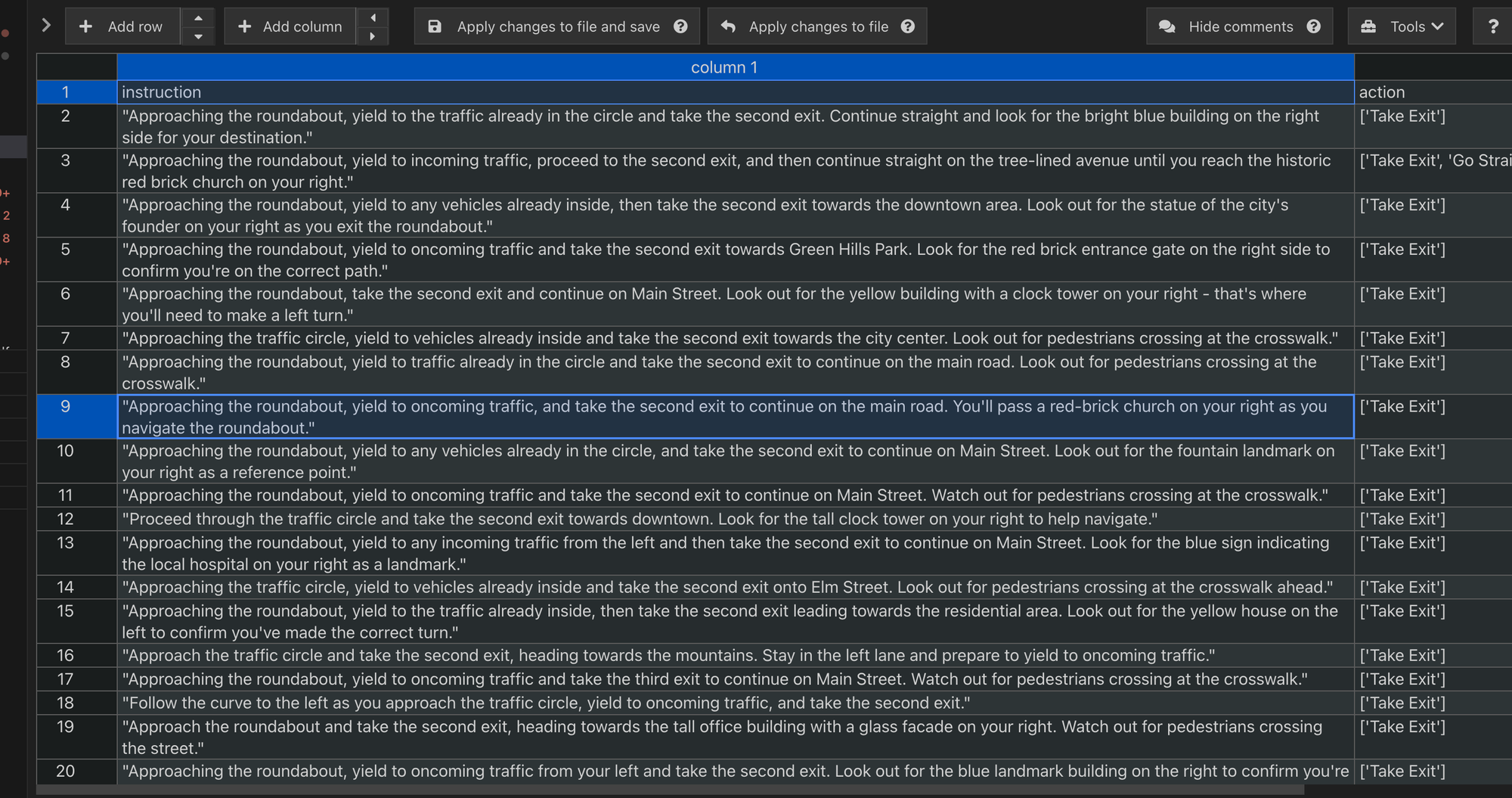
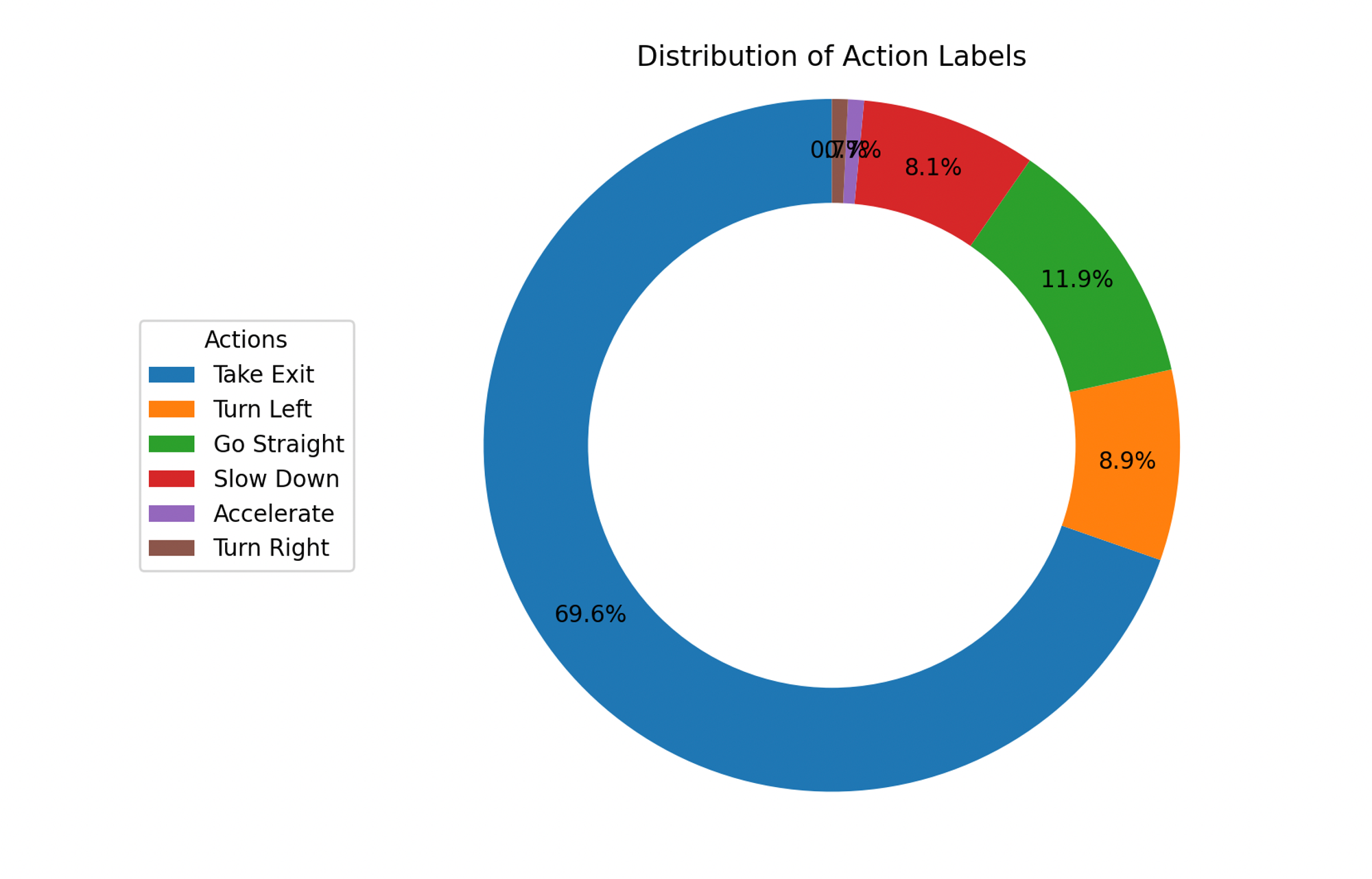
From the database analysis, we observed an increased presence of data duplicates, such as the instruction “Approaching the roundabout.” Consequently, the model’s interpretation of this instruction has predominantly skewed towards “take exit.” This repetition is also evident in the word cloud, where several words appear repeatedly. This issue results in an unbalanced distribution of data, which affects the model’s performance and accuracy in understanding diverse driving instructions.
Although the BERT model achieved satisfactory accuracy, the skewed data distribution poses challenges for real-world application. The model’s performance might not generalize well to new, unseen data if it does not reflect a balanced representation of all possible scenarios. This imbalance could lead to biased predictions and reduced effectiveness in practical use cases. Addressing this challenge will be crucial to ensure the robustness and reliability of the instructional generation system. Potential solutions include augmenting the dataset to ensure balance or applying bias correction methods during the model training phase.
Future Tasks
- Continue refining the data balancing strategies to further improve the diversity of generated outputs.
- Complete the integration and testing of additional commands from previous projects.
- Optimize the model training process and evaluate the effectiveness of the dataset division.