Coding week345 6/10-6/30
Weekly Meeting
In our recent meeting, we focused on enhancing our instruction generation process. I highlighted issues with data distribution, particularly the high similarity in GPT-generated data. To tackle this, we discussed strategies to balance our datasets, aiming to reduce redundancy and improve the diversity of the generated outputs. Sergio provided insights from previous projects, reviewing four key commands and proposing additional commands to enhance our current project’s functionality and efficiency. Additionally, we evaluated the metrics for our BERT model, agreeing that dividing the dataset into testing and training sets could yield acceptable results.
More details can be found here: Google Doc
Data Generation
Currently, although our dataset is relatively balanced, the randomness of the data is not high, leading to a significant amount of duplicate data. To address this issue and improve the diversity of GPT-generated instructions, we’ve identified several solutions:
Solution 1: Adjusting Parameters for Diversity
By fine-tuning the temperature and top_p parameters, we can enhance the diversity of generated instructions. The temperature parameter controls the randomness of predictions by scaling the logits before applying softmax. A higher temperature results in more random outputs. The top_p parameter, also known as nucleus sampling, which ensures that the model considers only the top p fraction of cumulative probability mass, thus allowing for a more focused yet diverse set of outputs. By carefully balancing these parameters, we can generate a broader range of unique instructions.
Solution 2: Increasing the Number of Samples Generated
Generating a larger number of samples and then filtering out unique instructions can effectively increase diversity. This approach includes:
- Generating More Samples: Produce a higher volume of samples than needed, ensuring a wide variety of potential instructions.
- Dynamic Batch Size: Implement a dynamic batch size that adjusts according to the remaining number of samples to be generated. To avoid hard-coding the batch size, it is set to twice the number of remaining samples, but not exceeding 50. This flexibility ensures efficient use of resources while maintaining the target number of unique instructions.
- Collection De-duplication: Utilize collection auto-de-duplication to filter out duplicate instructions. After de-duplication, limit the collection to the desired number of unique instructions. This process ensures that the final set of instructions is both diverse and manageable.
Solution 3: Adding Contextual Information
Incorporating more contextual information into the prompts can help the model generate more diverse instructions. Providing detailed context allows the model to understand the nuances of the task better, leading to richer and more varied outputs. This could involve including specific scenarios, additional background information, or detailed task descriptions within the prompts. By doing so, we enable the model to generate instructions that are not only diverse but also more relevant and contextually appropriate.
Iteration Method Example
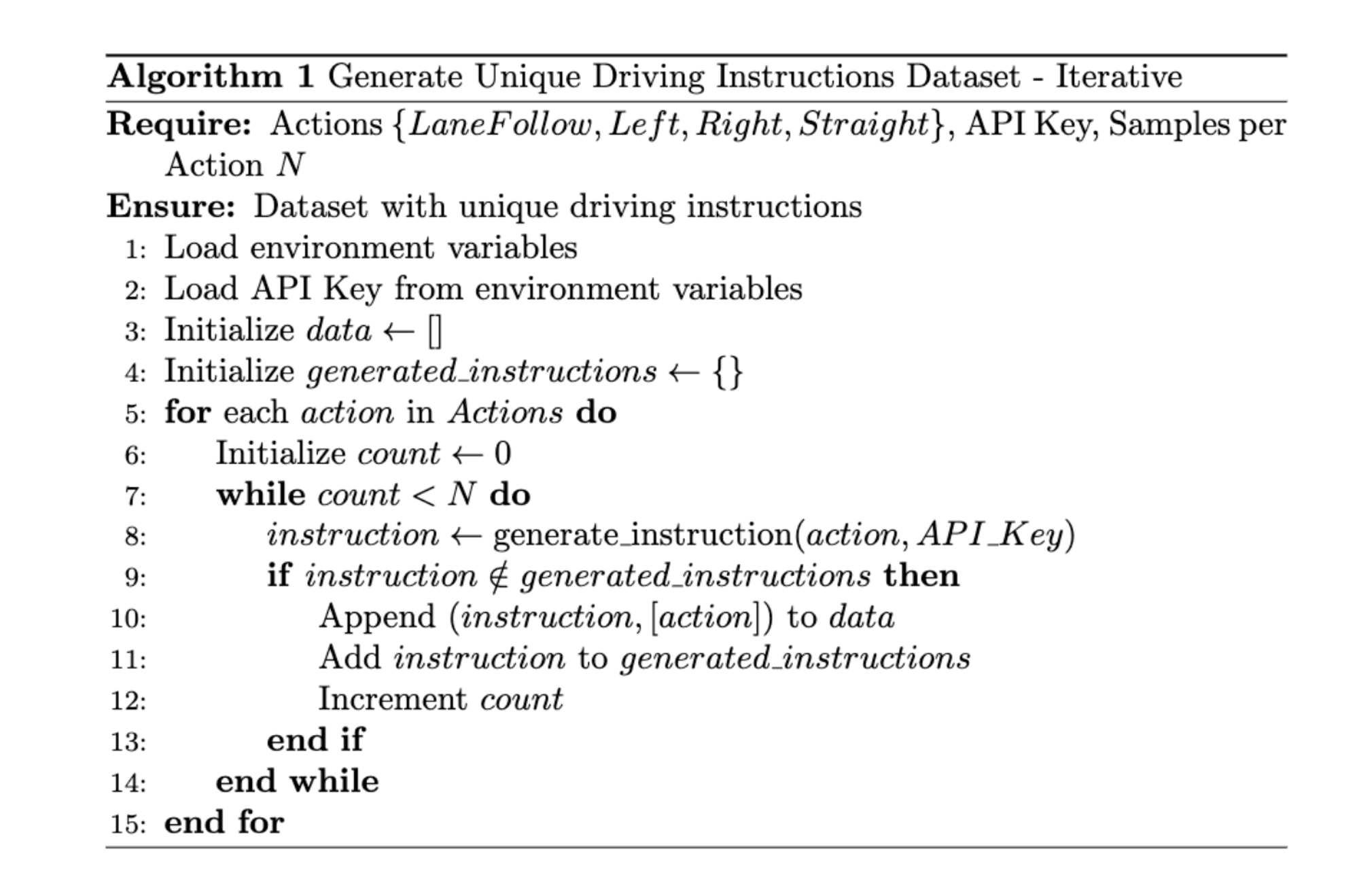
In one iteration, generating unique instructions for the action ‘LaneFollow’ involved multiple steps.
Similarly, generating instructions for actions like ‘Left’, ‘Right’, and ‘Straight’ required repeated attempts to reach the desired count of unique instructions, resulting in high redundancy and a longer processing time.
Action 'LaneFollow': Generated 1 / 25 unique instructions
Action 'LaneFollow': Generated 2 / 25 unique instructions
Action 'LaneFollow': Generated 3 / 25 unique instructions
Action 'LaneFollow': Generated 4 / 25 unique instructions
Action 'LaneFollow': Generated 5 / 25 unique instructions
Action 'LaneFollow': Generated 6 / 25 unique instructions
Action 'LaneFollow': Generated 7 / 25 unique instructions
Action 'LaneFollow': Generated 8 / 25 unique instructions
Action 'LaneFollow': Generated 9 / 25 unique instructions
Action 'LaneFollow': Generated 10 / 25 unique instructions
Action 'LaneFollow': Generated 11 / 25 unique instructions
Action 'LaneFollow': Generated 12 / 25 unique instructions
Action 'LaneFollow': Generated 13 / 25 unique instructions
Action 'LaneFollow': Generated 14 / 25 unique instructions
Action 'LaneFollow': Generated 15 / 25 unique instructions
Action 'LaneFollow': Generated 16 / 25 unique instructions
Action 'LaneFollow': Generated 17 / 25 unique instructions
Action 'LaneFollow': Generated 18 / 25 unique instructions
Action 'LaneFollow': Generated 19 / 25 unique instructions
Action 'LaneFollow': Generated 20 / 25 unique instructions
Action 'LaneFollow': Generated 21 / 25 unique instructions
Action 'LaneFollow': Generated 22 / 25 unique instructions
Action 'LaneFollow': Generated 23 / 25 unique instructions
Action 'LaneFollow': Generated 24 / 25 unique instructions
Action 'LaneFollow': Generated 25 / 25 unique instructions
Action 'Left': Generated 1 / 25 unique instructions
Action 'Left': Generated 2 / 25 unique instructions
Action 'Left': Generated 3 / 25 unique instructions
Action 'Left': Generated 4 / 25 unique instructions
Action 'Left': Generated 5 / 25 unique instructions
Action 'Left': Generated 6 / 25 unique instructions
Action 'Left': Generated 7 / 25 unique instructions
Action 'Left': Generated 8 / 25 unique instructions
Action 'Left': Generated 9 / 25 unique instructions
Action 'Left': Generated 10 / 25 unique instructions
Action 'Left': Generated 11 / 25 unique instructions
Action 'Left': Generated 12 / 25 unique instructions
Action 'Left': Generated 13 / 25 unique instructions
Action 'Left': Generated 14 / 25 unique instructions
Action 'Left': Generated 15 / 25 unique instructions
Action 'Left': Generated 16 / 25 unique instructions
Action 'Left': Generated 17 / 25 unique instructions
Action 'Left': Generated 18 / 25 unique instructions
Action 'Left': Generated 19 / 25 unique instructions
Action 'Left': Generated 20 / 25 unique instructions
Action 'Left': Generated 21 / 25 unique instructions
Action 'Left': Generated 22 / 25 unique instructions
Action 'Left': Generated 23 / 25 unique instructions
Action 'Left': Generated 24 / 25 unique instructions
Action 'Left': Generated 25 / 25 unique instructions
Action 'Right': Generated 1 / 25 unique instructions
Action 'Right': Generated 2 / 25 unique instructions
Action 'Right': Generated 3 / 25 unique instructions
Action 'Right': Generated 4 / 25 unique instructions
Action 'Right': Generated 5 / 25 unique instructions
Action 'Right': Generated 6 / 25 unique instructions
Action 'Right': Generated 7 / 25 unique instructions
Action 'Right': Generated 8 / 25 unique instructions
Action 'Right': Generated 9 / 25 unique instructions
Action 'Right': Generated 10 / 25 unique instructions
Action 'Right': Generated 11 / 25 unique instructions
Action 'Right': Generated 12 / 25 unique instructions
Action 'Right': Generated 13 / 25 unique instructions
Action 'Right': Generated 14 / 25 unique instructions
Action 'Right': Generated 15 / 25 unique instructions
Action 'Right': Generated 16 / 25 unique instructions
Action 'Right': Generated 17 / 25 unique instructions
Action 'Right': Generated 18 / 25 unique instructions
Action 'Right': Generated 19 / 25 unique instructions
Action 'Right': Generated 20 / 25 unique instructions
Action 'Right': Generated 21 / 25 unique instructions
Action 'Right': Generated 22 / 25 unique instructions
Action 'Right': Generated 23 / 25 unique instructions
Action 'Right': Generated 24 / 25 unique instructions
Action 'Right': Generated 25 / 25 unique instructions
Action 'Straight': Generated 1 / 25 unique instructions
Action 'Straight': Generated 2 / 25 unique instructions
Action 'Straight': Generated 3 / 25 unique instructions
Action 'Straight': Generated 4 / 25 unique instructions
Action 'Straight': Generated 5 / 25 unique instructions
Action 'Straight': Generated 6 / 25 unique instructions
Action 'Straight': Generated 7 / 25 unique instructions
Action 'Straight': Generated 8 / 25 unique instructions
Action 'Straight': Generated 9 / 25 unique instructions
Action 'Straight': Generated 10 / 25 unique instructions
Action 'Straight': Generated 11 / 25 unique instructions
Action 'Straight': Generated 12 / 25 unique instructions
Action 'Straight': Generated 13 / 25 unique instructions
Action 'Straight': Generated 14 / 25 unique instructions
Action 'Straight': Generated 15 / 25 unique instructions
Action 'Straight': Generated 16 / 25 unique instructions
Action 'Straight': Generated 17 / 25 unique instructions
Action 'Straight': Generated 18 / 25 unique instructions
Action 'Straight': Generated 19 / 25 unique instructions
Action 'Straight': Generated 20 / 25 unique instructions
Action 'Straight': Generated 21 / 25 unique instructions
Action 'Straight': Generated 22 / 25 unique instructions
Action 'Straight': Generated 23 / 25 unique instructions
Action 'Straight': Generated 24 / 25 unique instructions
Action 'Straight': Generated 25 / 25 unique instructions
instruction action
0 "Enter the highway and LaneFollow the middle l... [LaneFollow]
1 "Continue straight on Main Street and LaneFoll... [LaneFollow]
2 "Enter the highway and LaneFollow the traffic ... [LaneFollow]
3 "Enter the highway and LaneFollow the traffic ... [LaneFollow]
4 "Once you enter the highway, activate LaneFoll... [LaneFollow]
.. ... ...
95 "Continue driving straight on Main Street for ... [Straight]
96 "Continue straight on the highway for 5 miles." [Straight]
97 "Continue driving straight on Main Street for ... [Straight]
98 "Continue driving straight on this road for an... [Straight]
99 "Continue driving straight on this road for tw... [Straight]
[100 rows x 2 columns]
Dataset generated and saved to 'dataset_1000.csv'
Generated 100 instructions in 221.16 seconds.
Batch Method Example
By contrast, using a batch method improves efficiency and reduces redundancy. For example:

Action 'LaneFollow': Generated 25 / 25 unique instructions
Action 'Left': Generated 17 / 25 unique instructions
Action 'Left': Generated 19 / 25 unique instructions
Action 'Left': Generated 21 / 25 unique instructions
Action 'Left': Generated 22 / 25 unique instructions
Action 'Left': Generated 23 / 25 unique instructions
Action 'Left': Generated 23 / 25 unique instructions
Action 'Left': Generated 25 / 25 unique instructions
Action 'Right': Generated 25 / 25 unique instructions
Action 'Straight': Generated 23 / 25 unique instructions
Action 'Straight': Generated 25 / 25 unique instructions
instruction action
0 "LaneFollow the vehicle in front of you as you... [LaneFollow]
1 "Continue LaneFollow on the highway for the ne... [LaneFollow]
2 "Once on the highway, LaneFollow and maintain ... [LaneFollow]
3 "Enter the highway and LaneFollow the middle l... [LaneFollow]
4 "Stay in the right lane and LaneFollow the veh... [LaneFollow]
.. ... ...
95 "Continue straight on the highway for 5 miles ... [Straight]
96 "Continue straight on this road for the next 2... [Straight]
97 "Continue straight on the highway for another ... [Straight]
98 "Continue driving straight on this road for th... [Straight]
99 "Continue driving straight on the highway for ... [Straight]
[100 rows x 2 columns]
Dataset generated and saved to 'dataset_1000.csv'
Generated 100 instructions in 158.48 seconds.
The batch method resulted in fewer duplicate instructions and a significant improvement in processing time.
- Iteration Method: Generated 100 instructions with 521 duplicates in 221.16 seconds.
- Batch Method: Generated 100 instructions with 122 duplicates in 158.48 seconds.
The batch method improved efficiency by 28.34% and reduced duplicates by 326.23% compared to the iteration method.
Data Analysis
In addition to optimizing the generation of instructions, I performed an analysis of the data distribution and created a word cloud to visualize the most frequently occurring terms. This analysis helped us understand the underlying patterns in the dataset and identify areas for improvement.
Data Distribution Analysis
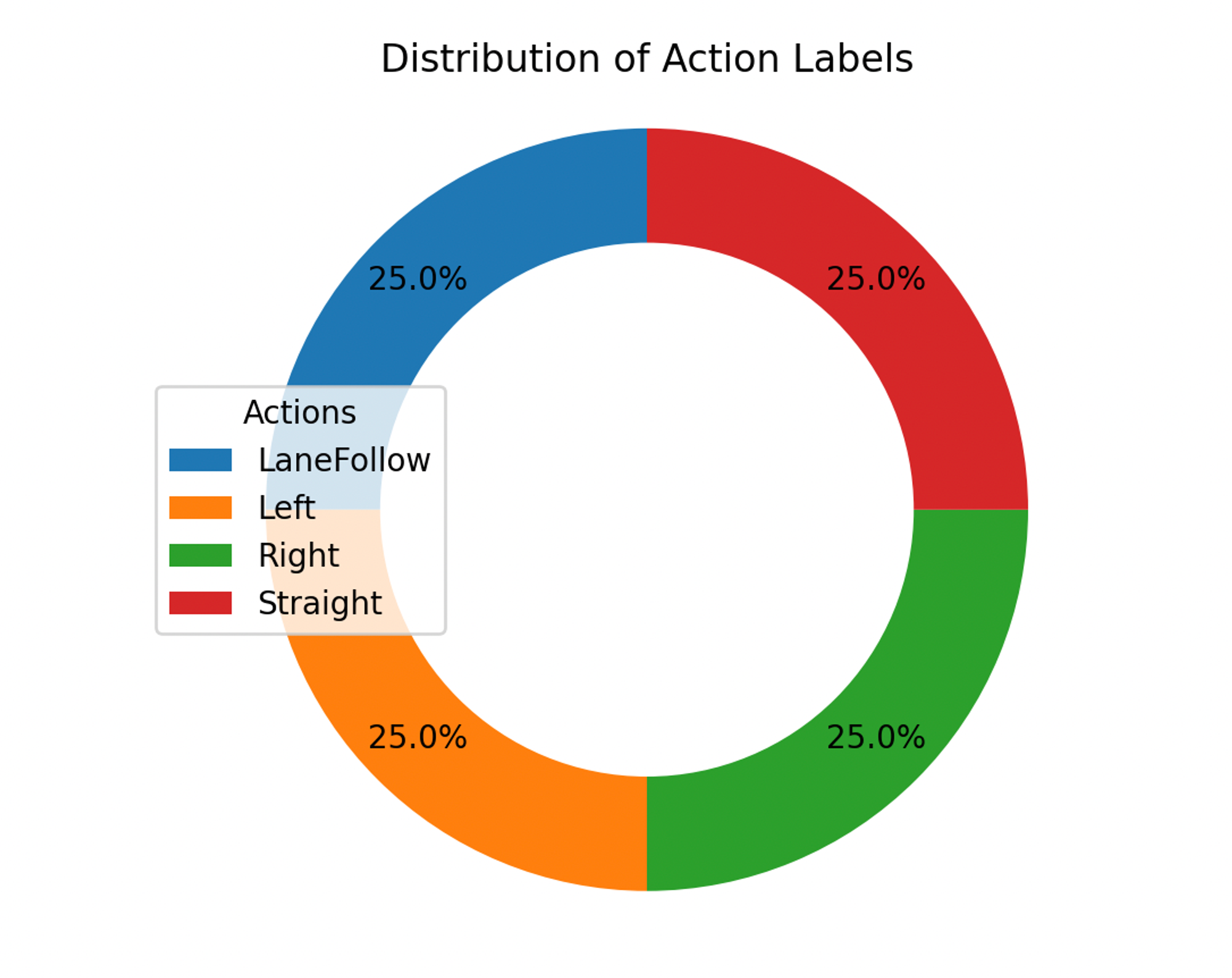
By examining the distribution of instructions across different actions, we identified four actions are balanced.
Word Cloud

The word cloud provided a visual representation of the most common terms in our dataset. Words like “continue,” “straight,” “left,” and “right” appeared frequently, indicating their prominence in the instructions. This visualization highlighted the need to diversify the vocabulary used in the generated instructions to enhance the overall richness and utility of the dataset.
Scalable of Datasets
print(f"Action '{action}': Generated {len(unique_instructions)} / {num_samples_per_action} unique instructions")
Action 'LaneFollow': Generated 43 / 125 unique instructions
Action 'LaneFollow': Generated 76 / 125 unique instructions
Action 'LaneFollow': Generated 112 / 125 unique instructions
Action 'LaneFollow': Generated 125 / 125 unique instructions
Action 'Left': Generated 17 / 125 unique instructions
Action 'Left': Generated 26 / 125 unique instructions
Action 'Left': Generated 31 / 125 unique instructions
Action 'Left': Generated 33 / 125 unique instructions
Action 'Left': Generated 40 / 125 unique instructions
Action 'Left': Generated 44 / 125 unique instructions
Action 'Left': Generated 47 / 125 unique instructions
Action 'Left': Generated 50 / 125 unique instructions
Action 'Left': Generated 50 / 125 unique instructions
Action 'Left': Generated 51 / 125 unique instructions
Action 'Left': Generated 54 / 125 unique instructions
Action 'Left': Generated 55 / 125 unique instructions
Action 'Left': Generated 57 / 125 unique instructions
Action 'Left': Generated 58 / 125 unique instructions
Action 'Left': Generated 60 / 125 unique instructions
Action 'Left': Generated 61 / 125 unique instructions
Action 'Left': Generated 63 / 125 unique instructions
Action 'Left': Generated 65 / 125 unique instructions
The implication of our current approach is that approximately 98% of the instructions generated in each batch will be discarded. This high discard rate indicates an inherent limitation in the method, where repeated looping of a prompt leads to a significant number of duplicate instructions. This issue highlights the challenges associated with maintaining diversity and uniqueness in large-scale instruction generation.
While we have successfully addressed issues related to small-scale data generation, balancing the dataset, and reducing data duplication, the challenge of data scaling remains unresolved. Scaling up our data generation processes without compromising diversity and quality is a complex problem that requires further exploration. If there is a demand for online large-scale data generation, we will need to develop and implement new strategies to handle these challenges. This may involve advanced techniques for dynamic prompt generation, more sophisticated filtering algorithms, and possibly leveraging real-time data augmentation methods to ensure a continuous stream of unique and varied instructions.