Coding week17 9/23-9/30
This week, I explored some works that integrate VQA with RL to enhance autonomous driving. This approach involves utilizing LLMs and transformer-based architectures to generate questions and responses based on driving scenarios.
VQA in Autonomous Systems
VQA leverages visual data to answer user-generated questions. In the context of autonomous driving, VQA can help process and analyze visual data, transforming real-time scenarios into structured interactions. For example, an autonomous vehicle using VQA might analyze traffic signals and generate questions regarding potential obstacles or safe navigation paths. VQA’s role in autonomous driving can be categorized into three core areas:
For VQA in autonomous systems, core aspects include image understanding and object detection, with model accuracy in recognizing pedestrians, vehicles, and road signs. Extensive datasets enhance model capability for object differentiation.
Additionally, contextual question generation offers support for decision-making, with relevant questions like “Is the pedestrian crossing clear?” at intersections aiding navigation. Real-time adaptability remains essential due to the dynamic nature of autonomous environments, which require high processing speeds and optimized algorithms to maintain safety and responsiveness without latency.
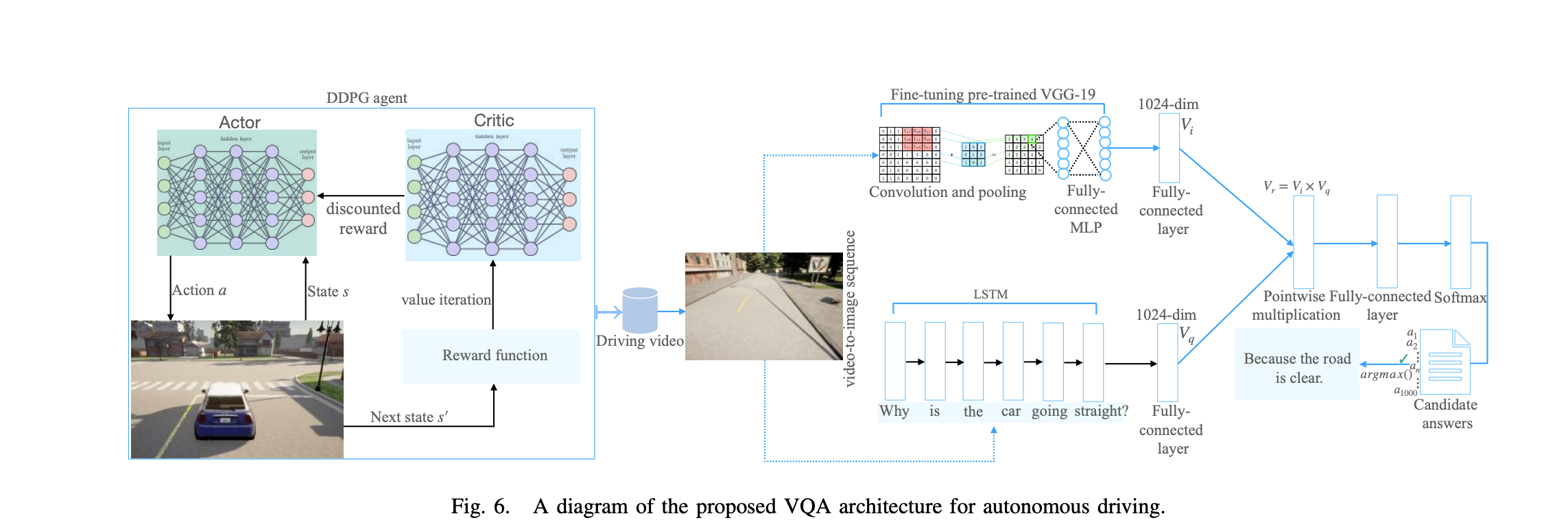
I delved into this paper
LINGO-1 and LINGO-2
LINGO-1 and LINGO-2
- Questionnaire-Based Interactions: Simulations that integrate VQA allow for the generation of scenario-specific questions. This approach improves user engagement and adds layers of safety by ensuring the system’s responses align with the scenario.
- Iterative Testing: By simulating various driving conditions, such as urban intersections or rural roads, researchers can test the adaptability of RL policies and refine VQA algorithms without risking real-world harm.
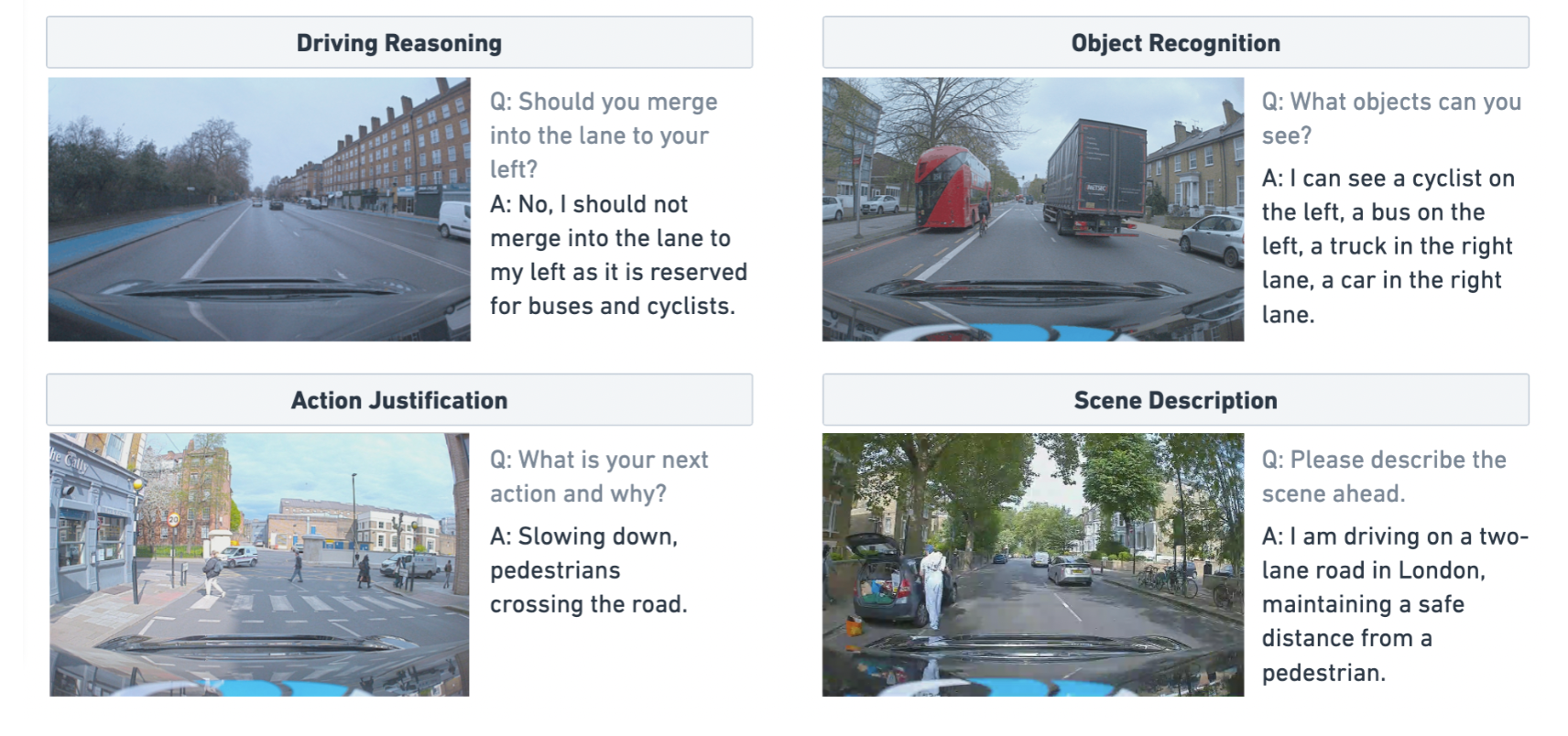
Action Items
Based on meeting insights, we will create a detailed technical plan, identifying open-source solutions for reproducibility testing.