Finally, my participation in the Google Summer of Code coming to its end. Whole summer me and my mentors have been developing completely new exercise for the Robotics Academy under the JdeRobot organization. From now on, students throught the globe can try their skills and learn something new while developing their solution to the exercise. As an outcome of the completion of the exercise, students will now learn how to work with Robot Operating System (ROS), its topics and services infrastructure, robot frames, and with some of its packages like move_base, AMCL, cmd_vel_mux. Student is now able to develop its own robot which completes quite challenging tasks like localization, mapping, global path planning, local navigation and also interesting behaviour of pallet’s pick and place. Now everything can be done by simply calling two command line commands!

Exercise structure
Exercise mainly consist of two (2) main files that need to be launched. One of them is a roslaunch file named amazonrobot_1_warehouse.launch. It basically initalializes the Gazebo world, spawns pallets and robot and after initializes the map_server, tf, move_base, and cmd_vel_mux nodes. All of them play a crucial role in robot operation and create required topics and transformations.
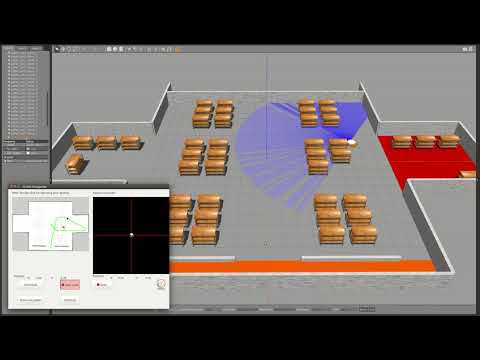
Next, amazonWarehouse.py Python script is launched to run the main robot operating algorithm and GUI interface. It looks as follows:

Script then subscribes to the required ROS topics and after can be used to operate a robot. Robot can be either operated by the teleop widget or by the MyAlgorithm API interface which sends commands to the move_base node. Additionally, robot’s pick behavior can be controlled in the same manner.
Solution example
This is one of the ways final solution to the exercise may look like:
The video shows the behavior of the robot, when the command to deliver particular pallet to the delivery zone was sent. Robot autonomously detects its location, picks and places at the required position. After, the robot navigates to the charging point, where it waits for further commands. Additionally, as it has been shown in the video, robot can be controlled by the teleop widget as well as with a special pick/place button, which should came in handy during solution development and debug process.
Final conclusions and thoughts
I earned a wonderful experience working on this project and want to address special thanks to my mentors Carlos and Alberto who supported and advised me during this summer, to the JdeRobot organization for allowing me to work with them, as well as to the Google company and its initiative for allowing me to focus solely on this project during this period. I have really learnt a lot new stuff about ROS, software project development and maintenance, Open Source software, and about teamwork. I am really proud of the results that have been achieved, and hoping that I’ll continue to contribute to the JdeRobot organization and release a second version of the exercise which is currently under development!
Thanks for your attention and have a good day!